| Napier Sabre |
| ||
|---|---|---|---|
| |
| ||
 |
|||
|
The Rolls Royce Vulture. | |||
|
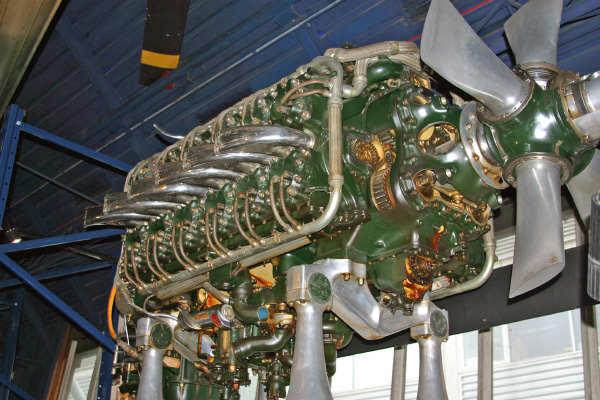
The Napier Sabre was a British H-24-cylinder, liquid cooled, sleeve valve, piston aero engine, designed by Major Frank Halford and built by Napier & Son during WWII. The engine evolved to become one of the most powerful inline piston aircraft engines in the world developing from 2,200 horsepower (1,640 kW) in its earlier versions to 3,000 hp (2,206 kW) by the end of the war.1
The first operational aircraft to be powered by the Sabre were the Hawker Typhoon and Hawker Tempest; however, the first aircraft powered by the Sabre was the Napier-Heston Racer, which was designed to capture the world speed record. Other aircraft using the Sabre were the Martin-Baker MB 3 prototype and one of the Hawker Fury prototypes. Later it became used in the early production of the Blackburn Firebrand. The rapid conversion to jet engines after the war led to the quick demise of the Sabre, because Napier also turned to developing jet engines | |||
|
The first Sabre engines were ready for testing in January 1938, although they were limited to 1,350 hp (1,000 kW). By March they were already passing tests at 2,050 hp (1,500 kW), and by June 1940 when the Sabre passed the Air Ministry 100-hour type-test, the first production-ready versions were delivering 2,200 hp (1,640 kW) from their 2,238 in³ (37 L). By the end of the year, they were producing 2,400 hp (1,800 kW). To put this in perspective, the contemporary 1940
Rolls-Royce Merlin II was generating just over 1,000 hp (750 kW).
By 1944, the Sabre V was delivering 2,400 hp (1,800 kW) consistently, and the reputation of the engine started to improve. This was the last version to see service, however, seeing service on the Hawker Typhoon and its derivative, the Tempest. Without the advanced supercharger, the engine's performance over 20,000 ft (6,100 m) fell off rapidly, and pilots flying Sabre-powered aircraft were generally instructed to enter fights only below this altitude. At low altitude, both planes were formidable, the Typhoon easily outpacing its German counterpart, the Focke-Wulf Fw 190. | |||
| Specifications: | |
|---|---|
| Napier Sabre | Date: | First Run 1938 |
| Cylinders: | 24 |
| Configuration: | H-24, Liquid cooled |
| Horsepower: | 2,200-3,000 hp |
| R.P.M.: | 3,700 rpm |
| Bore and Stroke: | 5 in (127 mm) x 4.8 in (120 mm) |
| Displacement: | 2,240 in³ (37 L) |
Endnotes:
|
1. Herschel Smith. The History of Aircraft Piston Engines. (Manhattan, Kansas; Sunflower University Press, 1986.) 91. |
Return To Engine Index.
© The Aviation History On-Line Museum.
All rights reserved.
Updated May 21, 2011.