|
 |
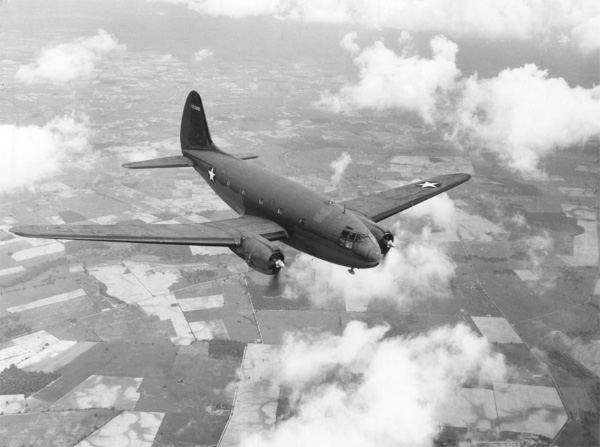
Curtiss C-46 Commando by Scott Schwartz |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
 |
||
|
Billed by Curtiss as the “Sub-Stratosphere Transport”, the airplane that became the C-46 military transport was actually intended to be a 36 passenger airliner with a pressurized cabin. It was an attempt to compete with that other famous airliner of the 1930’s - the Douglas DC-3.
Called the “CW-20T” by Curtiss, the prototype first flew in March of 1940. The CW-20T had twin vertical stabilizers and was powered by two Wright R-2600 14 cylinder engines producing 1,600 horsepower each, and turned three blade Hamilton-Standard constant speed propellers. |
| After initial flight testing, the twin tail arrangement was replaced by a single vertical stabilizer, and testing revealed that the CW-20 had some promise as an airliner. Whether it would have posed a threat to the Douglas DC-3'S market share is debatable. On paper, the CW-20 seemed much more capable than the DC-3, with greater fuel capacity, more seats, and a higher service ceiling. However the CW-20’s larger engines used more fuel, which limited the aircraft’s range. All of this, however, is academic, as the U.S. was gearing up for war. |
|
September, 1940 saw the U.S. Army order 200 CW-20B’s, which were designated as C-46’s. The first 25 C-46’s were basically civilian aircraft that were slightly modified for military use. The 26th aircraft to come off the production line was the first C-46 “A” version, which in turn was the first true military version of the aircraft. It was powered by the Pratt & Whitney R-2800 engine, producing 2,000 horsepower. Ironically, this was the engine originally intended for the airplane. Other changes included: replacement of the Hamilton-Standard propellers with four blade Curtiss Electrics, no cabin pressurization (although the airplane retained its service ceiling of 22,000 feet – no doubt due to the two stage supercharger equipped engines – a vestige of the airplane’s pressurized airliner roots), a reinforced cargo floor, and extra large cargo doors on the fuselage. Although 17 different variants of the airplane were produced, the C-46A and C-46F made up the bulk of the production run. A total of 3140 Commandos were made before production ended in 1946.
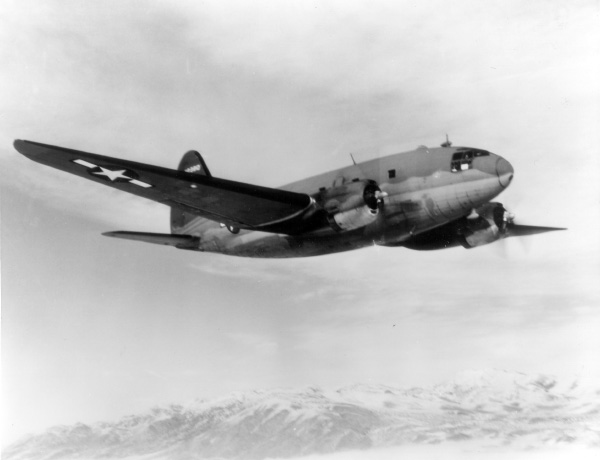

Initially, the C-46 was used to ferry cargo across the South Atlantic. It also saw some use as a glider tug in the European theatre. However, the C-46 became famous for its use in the China-Burma-India (CBI) Theater, flying supplies over Himalaya Mountains, otherwise known as “the Hump”. By March of 1942, the Japanese had control of nearly all of the supply routes through the area. Consequently, all of the supplies needed by Chiang Kai-Shek and Claire Chennault (who in June of that year became General Chennault when his American Volunteer Group was absorbed into the U.S. Army Air Forces), including aviation gasoline had to be flown in to China. Some of the terrain in the area rises to over 14,000 feet. The route was initially flown by C-47’s that were equipped with two stage superchargers, and C-87’s, which were cargo versions of the B-24. The C-87 retained the long range and high altitude operating capability of its B-24 cousin. It also retained the B-24's basic fuselage, the interior of which was 33 feet long, 4 feet wide and 8 feet high. While the C-87 could lift heavier loads than the C-46 and featured more “head room”, the narrow bomber-type fuselage made it difficult to carry large cargo items, even with the addition of a cargo door. Perhaps the most famous cargo aircraft of World War II, the C-47’s cargo area was wider than the C-87’s, but its maximum loaded weight was only 26,000 pounds.

On the other hand, the cargo area in the C-46 was 48 feet long, 9 feet, 10 inches wide, and 6 feet, 8 inches high. Its maximum loaded weight was 45,000 pounds (which could be pushed to 50,000 pounds). Not surprisingly, the C-46 became the mainstay of the CBI cargo route because of its combination of range, payload, and high altitude capability. Even with a capable cargo airplane such as the C-46, the Hump route was fraught with danger. There were enemy planes to contend with, (legend has it that a C-46 crew member shot a Zero down by firing his rifle though an open cockpit window.), the departure airfields in India were hot and humid, and the monsoon season was a killer. Literally. The demand for supplies was so great, that pilots were expected to fly under conditions that would normally ground airplanes based elsewhere. Accidents were common. Water leaked into cockpits through gaps in the window panes. In addition, navigation aids were scarce, and the airplanes were forced to operate near their limits. Even in an airplane such as the C-46, which was designed to fly at high altitudes, high altitude flying was a strain on engines, equipment and aircrews. Superchargers and/or engines failed on occasion, equipment malfunctioned, and keeping a non-pressurized cockpit heated was a challenge. The four hour flight under such dangerous conditions exhausted pilots and aircrew. Not to mention the fact that the airplanes were often overloaded. If all of the foregoing wasn’t bad enough, consider the fact that the C-46’s Curtiss Electric propellers had a nasty tendency to suddenly shift into flat pitch by themselves. This was due, in part, to humidity corroding the wiring associated with the propellers. Despite the hazards and losses, the C-46 had flown hundreds of tons of cargo by the time operations ended in November of 1945. Given its utility during the war, it should come as no surprise that the C-46 was used quite extensively afterward. Small cargo operators scooped up surplus Commandos and used them to ply the non-scheduled routes. Plus, the airplane was perfect for operation in the rough terrain found in parts of South America, such as the Amazon jungle and the Andes Mountains. The C-46’s military career didn’t end with World War Two. The United States used the C-46 (along with some other World War Two types) to fly missions during the Korean War and the CIA used it during the Bay of Pigs invasion. Still, age and wear have taken their toll, and there are only around a dozen Commandos still flying today. Two of them are operated by the Commemorative Air Force. |
| Specifications: | |
|---|---|
| Curtiss C-46 Commando | |
| Dimensions: | |
| Wing span: | 108 ft 0 in (32.91 m) |
| Length: | 76 ft 4 in (23.26 m) |
| Height: | 21 ft 9 in (6.62 m) |
| Weights: | |
| Empty: | 29,485 lb (13,374 kg) |
| Gross Weight: | 40,000 lb (18,144 kg) |
| Performance: | |
| Maximum Speed: | 264 mph (424 km/h) |
| Cruise Speed: | 173 mph (278 km/h) |
| Rate of Climb: | 1,300 ft/min (396 m/min) |
| Service Ceiling: | 27,600 ft (8,412 m) |
| Range: | 2,300 miles (3,701 km) |
| Powerplant: | |
|
Two Pratt & Whitney R-2800-43 two-row 18-cylinder radial engines, 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) each. | |
Endnotes:
©Scott Schwartz. The Aviation History On-Line Museum.
All rights reserved.
Created December 10, 2009. Updated October 17, 2013.