|
 |
Lockheed XF-90 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
 |
|
|
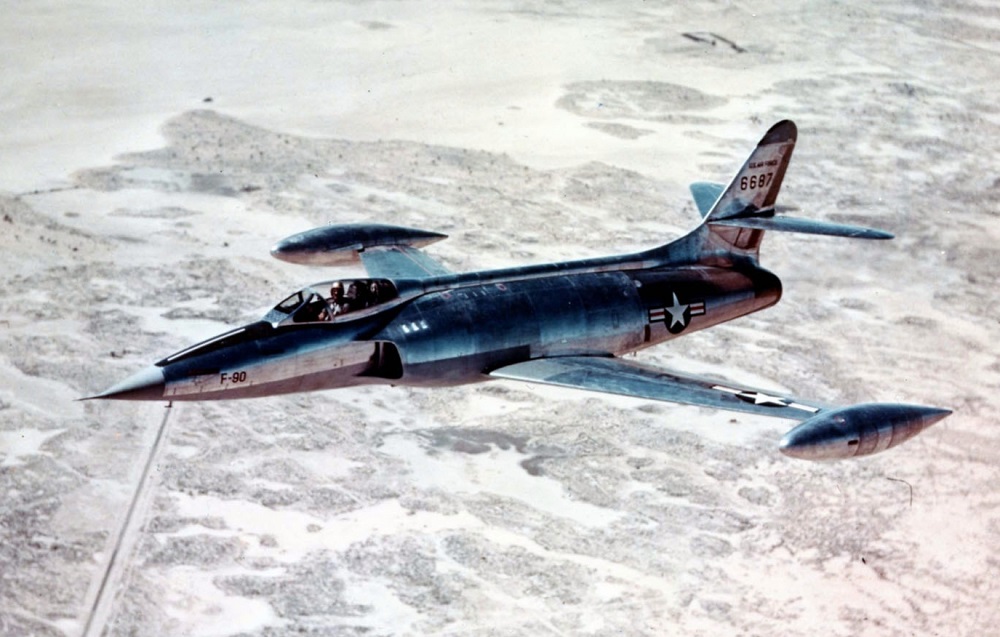
One of the hottest looking fighters ever to be built, but not go into production was the Lockheed XF-90. It was the first U.S. built, swept-wing jet to be equipped with afterburners and wingtip fuel tanks as standard equipment and have fully adjustable vertical and horizontal stabilizers. Fowler flaps and leading-edge slats improved airflow over the wings, making the F-90 one of the pioneers in 35-degree swept-wing technology. In tests, the XF-90 exceeded Mach 1 fifteen times. After World War II, the USAAF needed a “penetration fighter,” capable of escorting bombers to and from their targets. In 1945, the AAF issued a request for a fighter with a combat radius of about 900 miles. Competitors for the contract included McDonnell’s XP-88A, North American’s XP-86C, and Lockheed XP-90. (In 1948, the P designation for “pursuit,” was changed to F, for “fighter.”) Lockheed received a contract for two prototype XP-90s on June 20, 1946.1 Despite its sleek appearance, the XF-90 was pretty much of a dog when it came to performance. The reason was that it was way overbuilt and way underpowered. The plane was expected to exceed the sound barrier, but very little was known at the time as to what would happen. The aluminum skin was built with a stronger 75ST aluminum rather than the standard 24ST aluminum alloy, plus a greater thickness to make it four times more stress-resistant than standard construction. Weighing more than a DC-3, it was built to withstand 12 Gs, making it 80 percent heavier than the F-86. Additionally, it was seriously underpowered with its two J34 Westinghouse engines providing a total thrust of only 6,000 lbs (2,721 kgs) required to push 27,200 lbs (12,338 kgs) of aircraft. The thrust/weight ratio was only 22%.
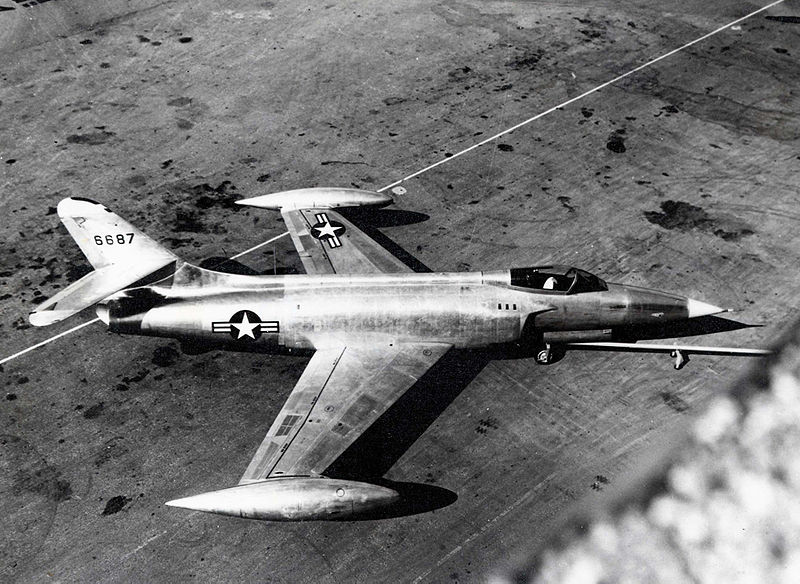

Although Chuck Yeager had broken the speed barrier on October 14, 1947 it was too late to be of any help with the design of the XP-90. On May 17, 1950, as the test program was conducting power-on dives to work up to the sound barrier, the aircraft made a dive at fairly low altitude and disappeared in the haze. At that same moment, ground observers heard a tremendous boom. They thought the airplane had exploded but to their relief, the airplane had dived to Mach 1.12 and everything was fine. It went on to exceed the sound barrier a number of times, and the XF-90 handled fine with no structural problems.


The XF-90 was a precursor to the "missile with a man in it," the F-104 Starfighter. It caught the nation's attention with its sleek looking design and made for splashy advertising for Westinghouse engines and was featured on the 1953 September cover of the comic book Blackhawk. Thereafter, the young baby boomer generation would be mesmerized with the coming of the jet age and each new adventure of the pilot Blackhawk and his buddy Chuck. This was the atomic age, where children lived in fear of nuclear attack and were taught to hide under their desk in schools during air raid rehearsals. With his squadron of six sleek F-90Bs, Blackhawk and his fighters would keep the threat of the Red aggressors at bay. Although Chuck Yeager had broken the sound barrier on October 14, 1947, it was too late to be of any help with the design of the XP-90. The ultimate winner of the competition was the McDonnell XF-88A Voodoo, and the XP-90 prototypes were left to an ignominious end. The first prototype was tested to destruction at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Laboratory in Cleveland and became scrap. The second prototype was sent to the Nevada Proving Ground for use in a nuclear weapons test and was subjected to three nuclear blasts. The explosions severed the tail and blew the landing gear from the wing; the main wing structure was buckled and scorched.2 In the late 1980s, the second prototype was recovered and decontaminated for preservation. It will be housed in the National Museum of the U.S. Air Force, near Dayton, Ohio. It is recognized for its importance played in the beginning of the cold war as an experiment in early atmospheric testing of atomic bombs. Its participation in three atmospheric atomic bomb tests helped in waging the cold war. The aircraft will be exhibited exactly as it sat, out in the desert for half a century.

The XF-90, as it sat in the dessert for half a century. |
| Specifications: | |
|---|---|
| Lockheed XF-90 | |
| Dimensions: | |
| Wing span: | 40 ft 0 in (12.19 m) |
| Length: | 56 ft 2 in (17.12 m) |
| Height: | 15 ft 9 in (4.80 m) |
| Weights: | |
| Empty: | 18,050 lb (8,187 kg) |
| Loaded Weight: | 27,200 lb (12,338 kg) |
| Max. Take-Off: | 31,060 lb (14,089 kg) |
| Performance: | |
| Maximum Speed: | 668 mph (1,075 km/h) @ 1,000 ft (305 m) |
| Cruise Speed: | 473 mph (761 km/h) |
| Climb: | 4.5 minutes to 25,000 ft (7,620 km) |
| Service Ceiling: | 39,000 ft (11,890 m) |
| Range: | |
| Normal: | 1,050 miles (1,690 km) |
| Maximum: | 2,300 miles (3,700 km) |
| Fuel Capacity: | |
| Normal: | 1,665 gal (6,303 lt) with supplemental tip tanks. |
| Powerplant: | |
|
Two 3,000 lb (1,361 kg) thrust Westinghouse J34-WE-11 turbojets. Modified to two 3,300 lb (1,633 kg) thrust Westinghouse J34-WE-15 turbojets with afterburner rating of 4,200 lb (1,905 kg) thrust. | |
| Armament: | |
| Proposed six .50 caliber machine guns. | |
Endnotes:
|
1. Rene J. Francillon, Lockheed Aircraft Snce 1913. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1987. 306. 2. Jorge and Karen Escalona. "Nukes vs. Airplanes." Air & Space Smithsonian. July 2008. |
©Larry Dwyer. The Aviation History On-Line Museum.
All rights reserved.
Created October 28, 2013. Updated May 24, 2023